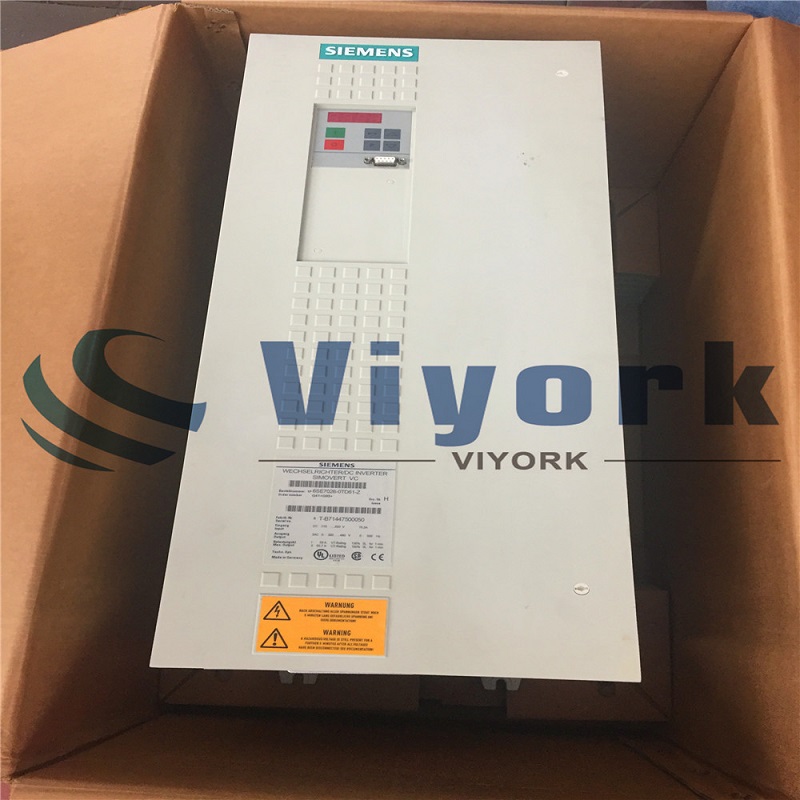
With the advancement of modern technology, the appearance of inverters has provided great convenience to everyone's lives. So what is an inverter? How does the inverter work? For friends who are interested in this, let’s come and find out together.
The inverter, one of many types of automation technology we own, converts DC power (battery, storage battery) into AC power (usually 220V, 50Hz sine wave). It is composed of the inverter bridge, control logic and filter circuit. It is widely used in air conditioners, home theaters, electric grinding wheels, electric tools, sewing machines, DVD, VCD, computers, TVs, washing machines, range hoods, refrigerators, video recorders, massagers, fans, lighting, etc. In foreign countries, because of the high popularity of automobiles, you can use inverters bought from reliable inverter suppliers to connect batteries to drive electrical appliances and various tools to work when you go out to work or travel.
Inverter is a DC to AC transformer, and it actually gives a rise to a voltage inversion process compared with the converter. The converter converts the AC voltage of the grid into a stable 12V DC output, and the inverter converts the 12V DC voltage output by the Adapter into high-frequency high-voltage AC; both parts also use a more used Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) technology. Its core part is a PWM integrated controller, Adapter uses UC3842, and inverter uses TL5001 chip. The operating voltage range of TL5001 is 3.6 to 40V, and there is an error amplifier, a regulator, an oscillator, a PWM generator with dead zone control, a low voltage protection circuit and a short circuit protection circuit in it.
Input interface part: The input part has 3 signals, 12V DC input VIN, working enable voltage ENB and Panel current control signal DIM. VIN is provided by the Adapter, and the ENB voltage is provided by the MCU on the main board. Its value is 0 or 3V. When ENB=0, the inverter does not work, and when ENB=3V, the inverter is in normal working state; while the DIM voltage is provided by the main board with a range of 0 to 5V. Different DIM values are fed back to the feedback terminal of the PWM controller. The current provided by the inverter to the load will also be different. The smaller the DIM value, the bigger the current output by the inverter.
Voltage start circuit: When ENB is high, it outputs a high voltage to light the panel's backlight tube.
PWM controller: It has the following functions: internal reference voltage, error amplifier, oscillator and PWM, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, short-circuit protection, output transistor.
DC conversion: The voltage conversion circuit is composed of MOS switch tube and energy storage inductor. The input pulse is amplified by the push-pull amplifier and then drives the MOS tube to switch, so that the DC voltage charges and discharges the inductor, and the other end of the inductor can obtain AC voltage.
LC oscillation and output circuit: It can ensure the 1600V voltage required for the lamp to start, and reduce the voltage to 800V after the lamp is started.
Output voltage feedback: When it is working with load, the sampled voltage is fed back to stabilize the voltage output of inverter.
 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  1103, Block C, South Building, Luo Fang Road, Luohu District, Shenzhen, 518001, China
1103, Block C, South Building, Luo Fang Road, Luohu District, Shenzhen, 518001, China